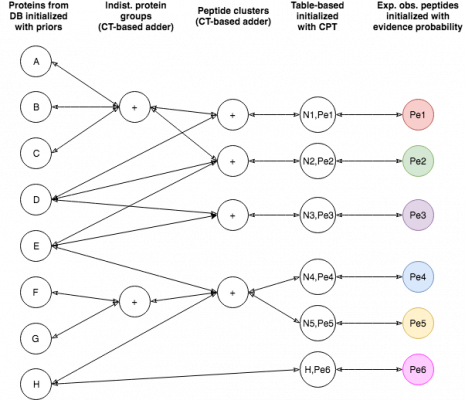
EPIFANY is a tool for efficient bayesian protein inference. It is included in OpenMS since 2.5. It takes one or more peptide database search engine results (in OpenMS' idXML format) that were post-processed by the PercolatorAdapter or IDPosteriorErrorProbability tool and adds posterior probabilities and/or false discovery rates for each protein or protein group to it.
Introduction
EPIFANY is a protein inference engine based on a Bayesian network. Currently, a similar model to Fido is used with the main parameters alpha (pep_emission), beta (pep_spurious_emission) and gamma (prot_prior). If not specified, these parameters are trained based on their classification performance and calibration via a grid search by simply running with several possible combinations and evaluating. Unless you see very extreme output probabilities (e.g. many close to 1.0 or 0.0) or you know good parameters (e.g. from an earlier run), grid search is recommended, although slower. The tool will merge multiple idXML files (union of proteins and concatenation of PSMs) when given more than one. This is useful for fractions or replicates if they were not merged already. It assumes one search engine run per input file but might work on more with undefined behavior. Proteins need to be indexed by OpenMS’s PeptideIndexer but this is usually done before Percolator/IDPEP since target/decoy associations are needed there already. Make sure that the input PSM probabilities are not too extreme already (garbage in – garbage out). After merging, the input probabilities are preprocessed with a low posterior probability cutoff to neglect very unreliable matches. Then the probabilities are aggregated with the maximum per peptide and the graph is built and split into connected components. When compiled with the OpenMP flag (default enabled in the release binaries) the tool is multithreaded which can be activated at runtime by the threads parameter. Note that peak memory requirements may rise when processing multiple components of the graph at the same time. The tool offers an option for a greedy group resolution which is helpful for reducing false-positive identifications in the presence of many shared peptides between present and non-present proteins. Note that it might reduce true positives, too and introduces a fake certainty by removing proteins without evidence after retaining only associations between a peptide and its best producing group (after probabilistic inference). The option is mainly suggested when protein inference is the last step of the analysis. A middle-ground between greedy resolution and standard (sum-product) inference is a regularized max-product inference (for this, set the regularize flag and choose a p-norm smaller than 0 [implying infinity]).
Update (February 2020) – Now in OpenMS 2.5+
EPIFANY can now also be found in the official OpenMS 2.5 release (or later). We recommend using the version that ships with your OpenMS distribution of choice. For the binary used in the publication, you can use the installation links and methods below or check out the source code from the corresponding GitHub tag.
Steps:
- Download the installer for your platform via the button above
- Install OpenMS following the Installation instructions
- After installation and adding the TOPP tools (including EPIFANY) to your global Path environment, you can start scripting. Follow the instructions here for some introduction to scripting with OpenMS
Steps:
- Download the KNIME installer for your platform via the button above
- Install KNIME
- After installation follow this small video tutorial to install the OpenMS plugin. Use the following update site URL for the copy-paste step in the video: https://abibuilder.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/knime-plugin/updateSite/experimental/feature/proteomic_lfq You can give it any name (e.g. OpenMS EPIFANY Update Site).
- You will then find EPIFANY (together with the other OpenMS nodes) in the node repository in the lower left of the program.
- You can create a new workflow with it or import the workflow for our example data. Don’t forget to configure Input File(s) to point to the files on your computer
System Requirements:
Install or build OpenMS (see OpenMS’ requirements at the bottom of the page). You can do it either standalone or as a KNIME plugin.
Command Line
Command line documentation of the tool can be found here (in the UTILS section of the OpenMS documentation under the tool’s name).
Limitations
Contradicting connected components may dictate runtime in certain parameter settings. Extensive parameter grid search is computationally expensive (may be reduced if there are good estimates).
Inputs
Direct input for the tool: An idXML file with indexed and target-decoy annotated proteins and peptides that carry probabilities (e.g. from OpenMS’ IDPosteriorProbability, Percolator, Peptide/iProphet…)
General input for a complete protein inference workflow: Centroided mzMLs from a bottom-up/shotgun data-dependent acquisition experiment. If your data is in “.raw” format you can do the conversion and centroiding with e.g. proteo-wizard (included in every OpenMS installation, too). Inputs can be replicates and/or fractions. Depending on your goals you could also merge conditions. We advise calculating peptide probabilities on a global (i.e. merged) level, as done in the example workflow.
Download sources and example data
Publication: J. Pfeuffer, T. Sachsenberg, T. M. Dijkstra, O. Serang, K. Reinert, and O. Kohlbacher, “EPIFANY-A method for efficient high-confidence protein inference,” Journal of proteome research, p. 734327, 2019.
Experimental installer downloads until it is merged into the OpenMS Release: OpenMS experimental archive
Example Data: You can use the converted mzMLs on our server as direct input to the KNIME workflow that is also linked there. The data comes from the iPRG2016 study (sample “B”). You can also use the merged idXML on the server for a direct input to EPIFANY.
Large-scale Example Data: An example for larger scale data can be found on the same server (bigDataProbabilities.idXML). Its raw files/mzMLs will be referenced after the dataset is published.
Example KNIME Workflow: Workflows implemented in KNIME are also found on the server. The outputs of the workflow are compatible with the evaluation script of the iPRG2016 study. Experimental update site for the plugin installation in KNIME (copy-paste when adding a new update site under Help->Install New Software): https://abibuilder.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/knime-plugin/updateSite/experimental/feature/proteomic_lfq
OpenMS implementation sources: github.com (Epifany.cpp and BayesianProteinInferenceAlgorithm class)
Inference library source: Evergreen